A traditional methodology for obtaining feedback and assessing the degree of customer loyalty, NPS is an important ally to improve the relationship with the consumer, but it will not bring satisfactory results if it is not applied efficiently.
Therefore, it is important to be aware of the best ways to set NPS goals, adopting some postures:
- Understand why predefined quality zones are not a good reference.In the absence of references, benchmarking data, many companies end up incorrectly using NPS “good practice” tables.
For example: Zone of Excellence – NPS between 75 and 100 Quality Zone – NPS between 50 and 74 Zone of Improvement – NPS between 0 and 49 Critical Zone – NPS between -100 and -1 Such tables are generalist and ignore important points that we must consider when setting goals.
Let’s go to them: a) SMART Goals
You may not know it yet, but the SMART technique is widespread worldwide and used to set goals.
S – Specific M – Measurable A – Attainable R – Relevant T – Time Based All points of SMART are important, but for the explanation of this text, the “A” for Attainable and the “R” for Relevant are the most relevant (to learn more about SMART click here).
All points of SMART are important, but for the explanation of this text, the “A” for Attainable and the “R” for Relevant are the most relevant (to learn more about SMART click here).
When we set a goal for the organization, we need to define something that is ATTAINABLE.
Otherwise, we generate frustration in everyone involved and the NPS program will fall into disrepute in the organization.
Now, imagine that one of your units has an NPS of 30 and you set a “Quality Zone” goal, with an NPS of 60.
There is some doubt that this unit will have difficulty in achieving the goal.
b) Benchmarking
Fred Reichheld, in his book “The Ultimate Question 2.0”, makes it very clear the importance of understanding what the references of your market are.
In other words, retail has an NPS benchmarking zone, the telecommunications area has another, and transportation, another.
So, if you need a relevant NPS benchmark to determine your long-term metrics, you need to understand what your segment’s NPS range is and where your brand stands.
Let’s assume that your company is a cable TV provider.
You set a goal within the “quality zone” (between 50 and 74), but as you can see below, this market in the United States in 2013 had a maximum NPS of 18.
In other words, setting the goal between 50 and 74 will probably only put the NPS project in disrepute, after all, this does not seem to be an attainable goal in the segment.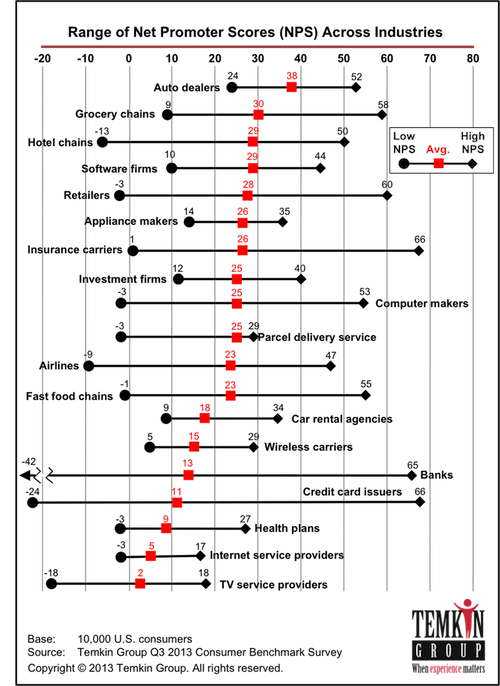 c) Research has bias The biggest influences in the case of NPS surveys are collection methods and channels.
c) Research has bias The biggest influences in the case of NPS surveys are collection methods and channels.
The topic of bias in satisfaction surveys is quite controversial.
There is always someone saying that changing the color of the survey buttons, the collection channel – or any other detail – can change the survey results.
I always join the discussion stating that it “cannot” change, but that it “will change”.
Below, in image 1, the impact of a very slight change in the survey collection method and, in image 2, the difference in NPS in the same brand, but in different channels.

- Step by step on how to set NPS goals:a) Measure the NPS of the brand, divisions, regions, each store and – when possible – each key employee involved in the transactions; b) Based on the results found and benchmarking in your segment, define achievable short, medium and long-term objectives for the organization’s overall NPS. Example: Brand Measurement Result in the 1st month: 50 Short-term (3 months): 60 → +10 points compared to the 1st month Mid-term (6 months): 70 → +20 points compared to the 1st month Long-term (12 months): 75 → +25 points compared to the 1st month Based on the organization’s overall goals, define the objectives of the units.
Example: Result of Unit 001 in the 1st month: 23 Short Term (3 months): 33 → +10 points in relation to the 1st month Medium Term (6 months): 43 → +20 points in relation to the 1st month Long Term (12 months): 48 → +25 points in relation to the 1st month Result of Unit 010 in the 1st month: 70 Short Term (3 months): 80 → +10 points compared to the 1st month Medium Term (6 months): 90 → +20 points compared to the 1st month Long Term (12 months): 95 → +25 points compared to the 1st month
In this way, it is possible to obtain results in a feasible and consistent way, making the use of NPS important for the constant improvement of customer relationships. by Tiago Serrano









